Legislation
The legislation module allows you to manage formal aspects in the company and facilitates the coordination of these activities. The module includes functions related to the audit mechanisms of ISO processes, but also to elements related to formal legal analyses.
The functions are available in the main menu in the 'Legislation' section.
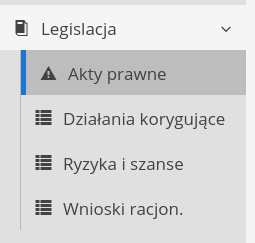
Legislation application menuThe following functions are available in the menu and module:
-
Legal acts - management of legal acts and the register of legal analyzes of the company’s activities.
-
Corrective actions - corrective actions
-
Risks and opportunities - register of risk and opportunity analyses
-
Rationalization proposals - register of rationalization proposals
Legal acts
Legal acts are a function of the system that enables the registration of documents and legal acts applicable to the company along with a full analysis of individual articles of the documents. The register allows for a formal analysis of these documents along with a register of justifications for the criticality of individual articles of documents on the company’s operations. This facilitates the analysis and demonstration of compliance with formal tasks regarding the correctness and compliance of the company’s operations with applicable legal acts. As an add-on, the system enables ongoing analysis of legal acts being created and published in the Journal of Laws and Monitor Polski, along with e-mail notification of new documents that meet any search criteria.
When you enter the module, you are presented with an empty initial view. A preliminary definition of legal contexts is required. We can do this via the edit button next to the selection list.
The main menu of the module contains actions for accessing dictionary data. They are required for the definition of initial data and dictionaries.
-
Contexts - definition of work contexts
-
Aspects - definition of aspects
-
Reminders - list of reminders defined in the module
Contexts
Context allows you to separate formal parts/documents into one whole. After selecting a section from the menu, a list of all contexts is presented.
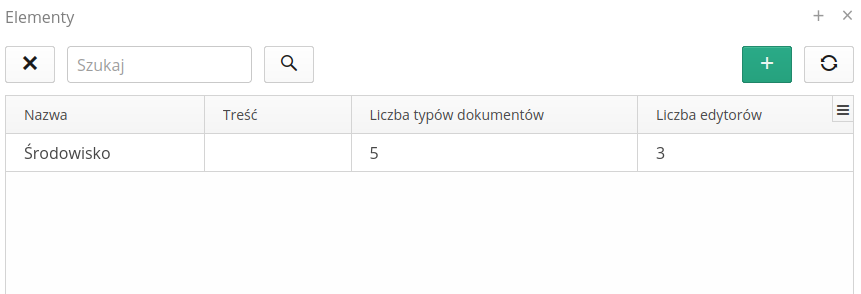
Adding a new context allows you to define the context and define access lists and division into document types.
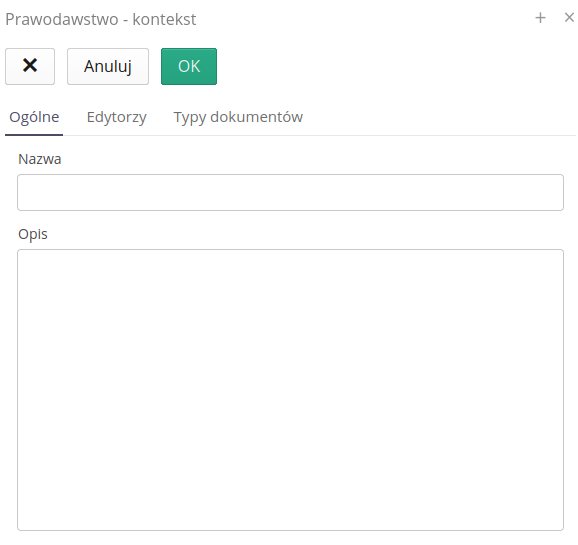
Available options and context definitions:
-
Name - context name
-
Description - detailed description of the context
-
Editors - a list of people who have access to a given context and can work on it
-
Document Types - a list of document types, e.g. "Journal of Laws", "EU legal acts", etc.
The document type allows you to define its basic parameters:
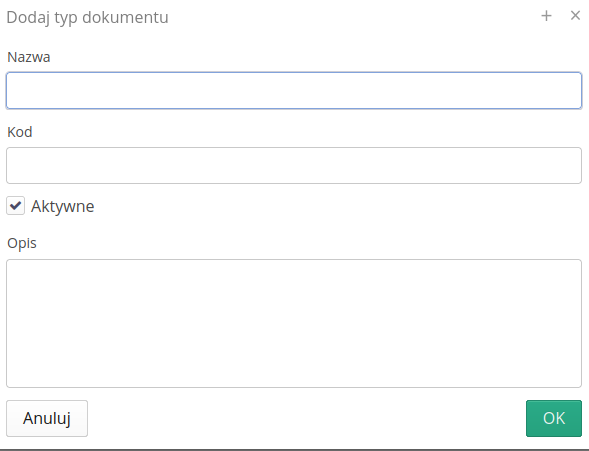
-
Name - type name
-
Code - code can be used for document analysis through integration with API programming interfaces
-
Active - whether a given document type is active in a given context
-
Description - description of the document type
After saving the new context, refresh the main view to see it in the list. Remember about the permissions in the Editors list for a given context. Otherwise, you will not see the given context.
|
Aspects
Legal aspects is a dictionary that allows you to categorize articles in documents. Entering the configuration displays a list of defined aspects and allows you to edit them/create new records.
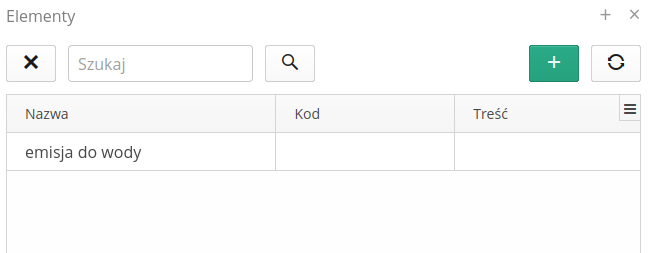
Adding a new aspect displays a form with available options:
-
Name - the name of the aspect
-
Code - code can be used for document analysis through integration with API programming interfaces
-
Description - description of the aspect
We use aspects in the definitions of individual articles of the document to additionally describe the validity and functions performed within a given article.
Reminders
Reminders are a mechanism that allows you to send a message at the right moment in time, which may concern the entire context of legal issues, a specific document or a specific article. It allows you to manage tasks within individual events and prevents you from omitting important issues within these tasks. Often articles or legal documents contain provisions that are required for verification when, for example, implementing acts are created. We can use reminders to make it easier for us to remember to do these things.
The list of all reminders is available in the module’s main menu. Shows all reminders pinned to any object in the system.
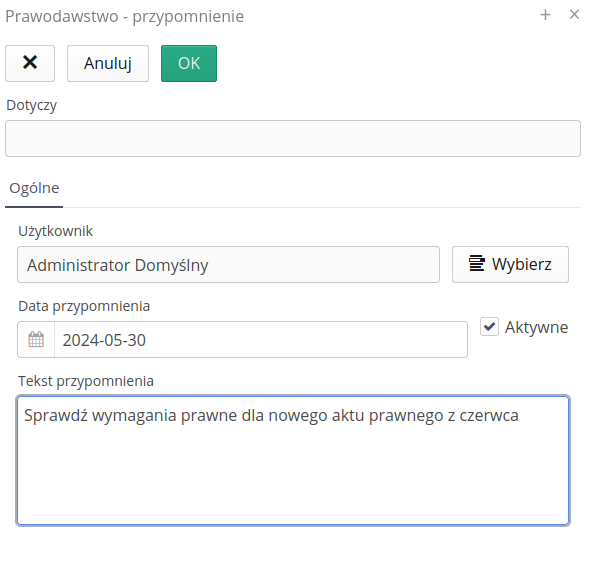
The new reminder editor allows you
-
Applies to - the context to which the reminder applies. Set automatically.
-
Active - whether the reminder is active and an email with its content will be generated
-
User - recipient of the reminder
-
Reminder date - the date when the reminder will be generated and sent
-
Content - the content of the reminder
| For the mechanism to work properly, an active scheduler is required in the system, which will generate information and send it to recipients. Using it, we can specify the hours at which these reminders will be sent. |
Documents
Once we have selected the context, we can start working on the documents. The view is displayed as a group of tabs that divide the document view according to document types defined in the context. Below is a list of documents of this type.
It is possible to enter new documents using the + Document button. The system will automatically add a new document to the list and allow you to edit it.
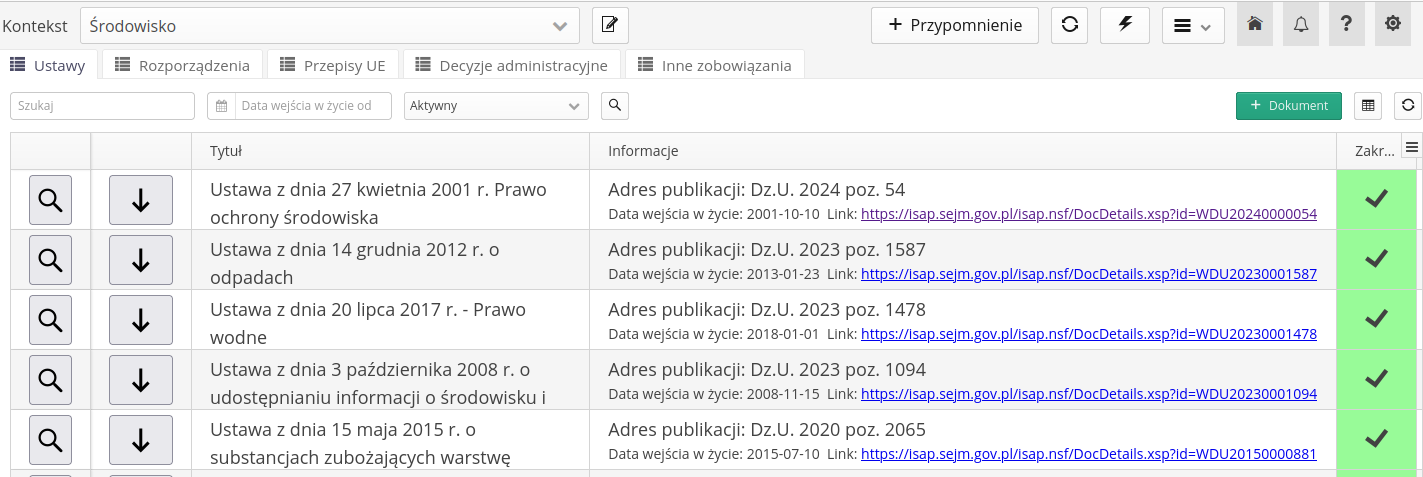
Filter fields are available at the top of the view. They consist of:
-
Search - search for any text within the entered data
-
Document date - defining the document validity filter
-
Status - filtering by document status
Additionally, there are buttons:
-
Export to XLS - export all data to XLS Excel format
-
Refreshing the data view
Each document is presented in a table with summary information regarding its content and a preliminary analysis of whether or not it is appropriate to deal with a given document within the organization
-
Preview - the button allows you to view the details of a given document within a drop-down list
-
Articles - displays a list of articles of a given document
-
Title - title of the document/legal act
-
Information - additional information about the document, including a link to the original publication of the document
-
The scope concerns - information and status whether a given document is required for analysis in the organization
After selecting the preview action, the user goes to preview/edit the given document. All changes to the fields are automatically saved by the system and an appropriate message appears in the information bar. Document details allow for all operations and field modifications.
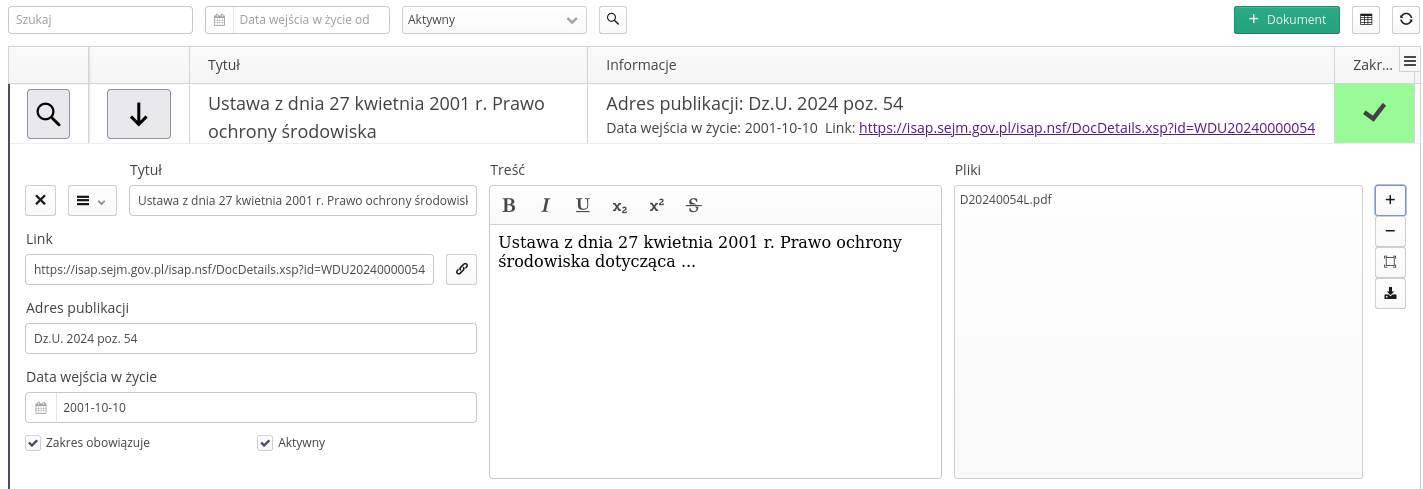
Possible changes/entries of data
-
Title - title of the document/legal act
-
Link - a link to an external website of the organization publishing it
-
Publication address - publication address, e.g. entry in the Journal of Laws of the Republic of Poland
-
Effective date - the date the document becomes effective
-
Scope valid - flag whether the scope of the document is valid in a given organization and should be referred to
-
Active - information about whether a given document should be visible in the default data view
-
Content - content/abbreviation of the document content
-
Files - list of additional attachments and data
The context menu in the details view allows for additional operations on a given document:
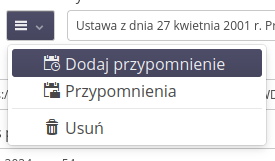
-
Add reminder - adding a reminder in the context of a specific document
-
Reminders - a list of all reminders for a given document
-
Delete - delete the document. ATTENTION. deleting a document also deletes all articles and attachments added as part of these operations
Additional buttons in the file list allow you to:
-
Add, delete, download a file - operations on the selected file or uploading new files/attachments to the document
-
File Preview - Preview PDF files in split view
After selecting the file preview, it opens in the side panel. The file is navigable and allows you to review the information in the file while working with the list of articles. This makes your work much easier and allows you to quickly enter data into the system. You can close the preview at any time and return to the default view.
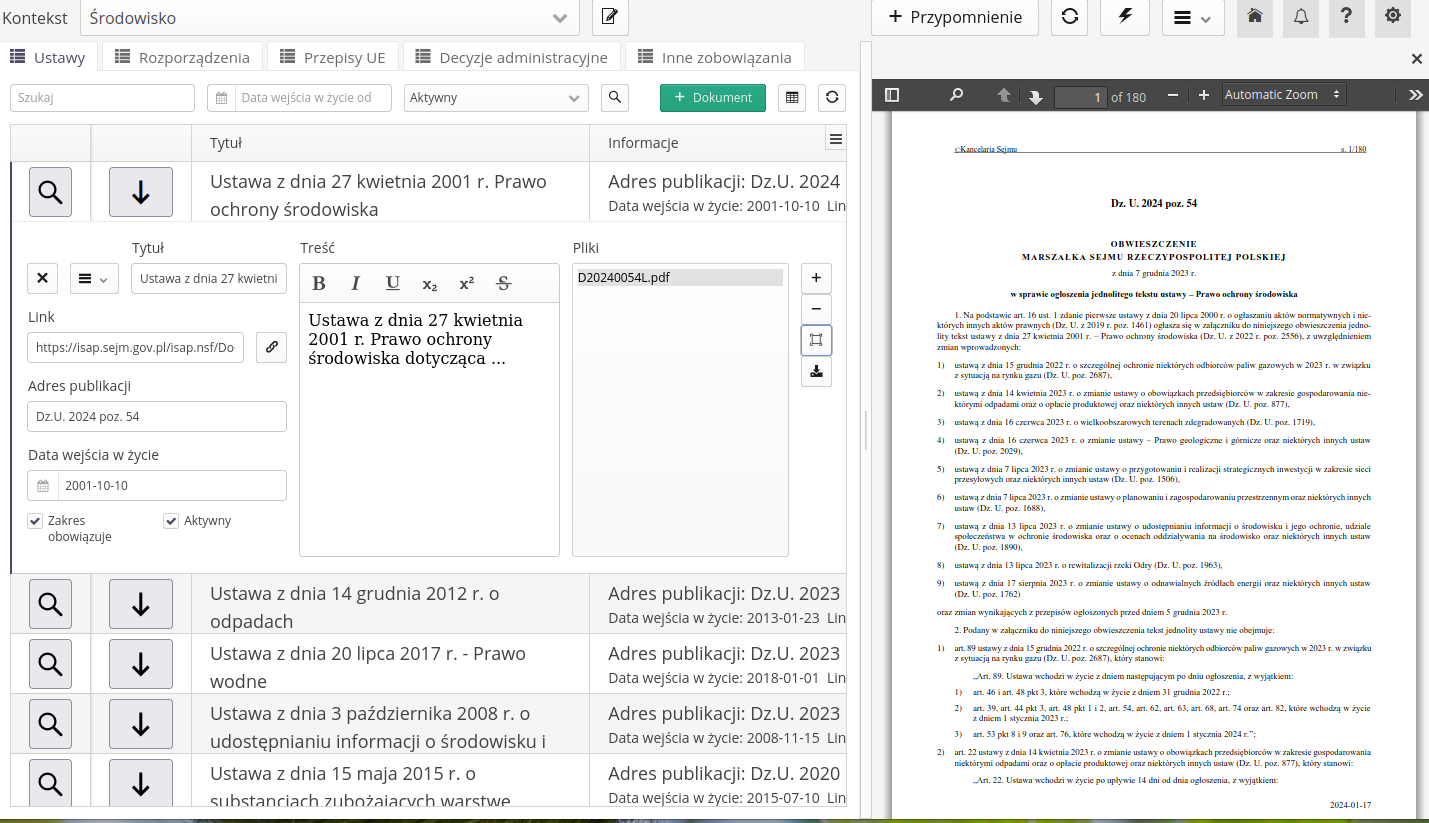
After selecting the list of articles - the down arrow button - the view changes to the list of articles. We add new articles using the + Add button. The system automatically opens the new article editing panel.
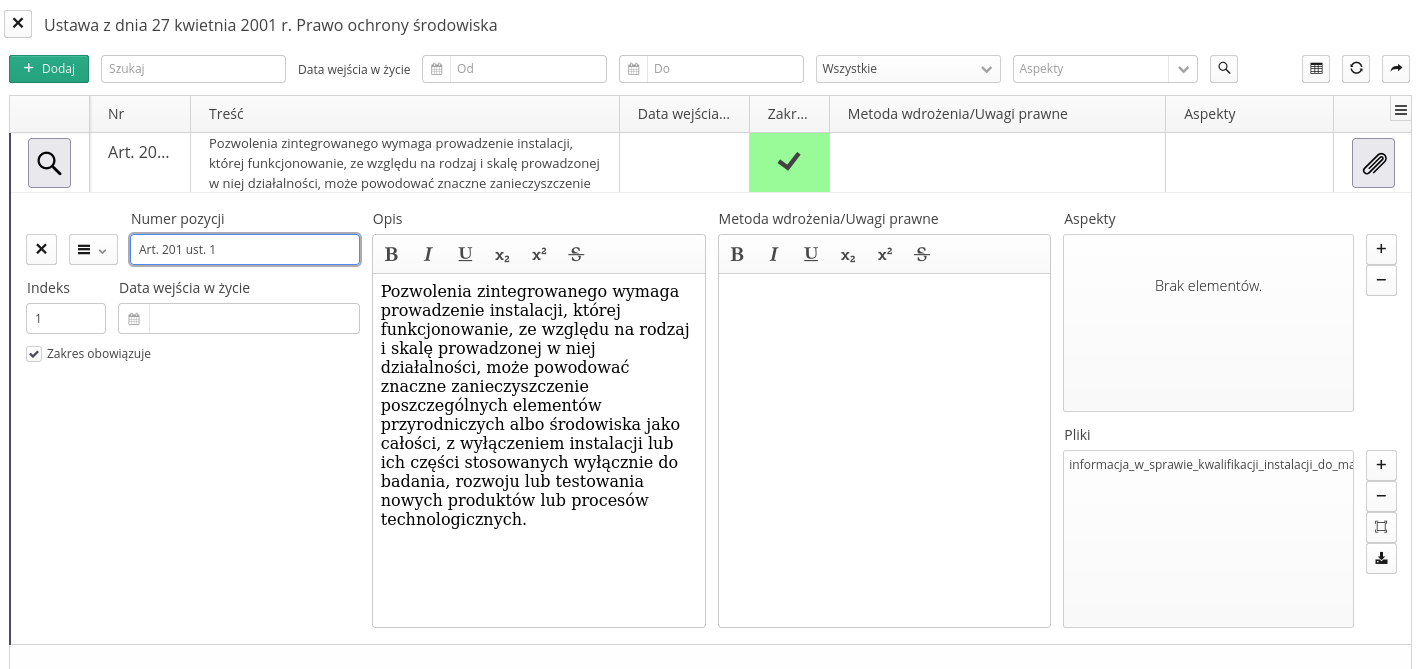
At the top of the view there is a bar of activities and tasks.

Available operations and filters
-
Add - adding a new article
-
Search - search box for any text in articles
-
Effective date from-to - filter of the dates when the article begins to come into force
-
Applicability - whether an article is valid in a given organization
-
Aspects - a filter list of aspects covered by the selected articles
-
Search - action to perform a search and update the view
-
XLS export - export of article data to the XLS Excel file format
-
Refresh - refreshes the view
-
View in new window - displaying the list of articles in a new, detached window
After selecting any article, a quick preview is displayed within a given list with the option of fully editing the information contained therein. Available operations and fields:
-
Menu - context menu of the article with additional actions
-
Item number - item number of the article in accordance with the formal provision in the legal act
-
Index - index is the number by which articles are sorted in the default view. It allows you to sort articles according to numerical order, regardless of the format and style of the Item Number description. The system automatically sorts articles by index and then alphabetically by item number.
-
Date of entry into force - the date a given article enters into force
-
Scope is valid - whether the scope of the article is valid in a given organization
-
Description - article description/information summary
-
Implementation method/legal notes - description of the implementation method and legal information required to implement a given article
-
Aspects - a list of aspects covered by a given article
-
Files - additional attachments, explanations or additional information
All changes you make to the fields are automatically saved in the background and an appropriate message appears.
The article context menu contains additional actions related to the article:
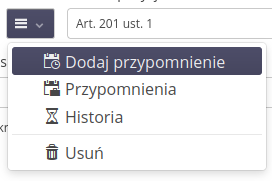
-
Move up - moves the article up the list
-
Move down - moves the article down the list
-
Add above - adding a new article above the current one
-
Add below - adding a new article below the current one
-
Add reminder - adding a reminder in the context of a specific article
-
Reminders - a list of all reminders for a given article
-
History - history of changes to the article
-
Delete - delete the article
After selecting change history, a list of all changes and current field values in a given article is presented. This allows for retrospective analysis of changes and information entered by users.
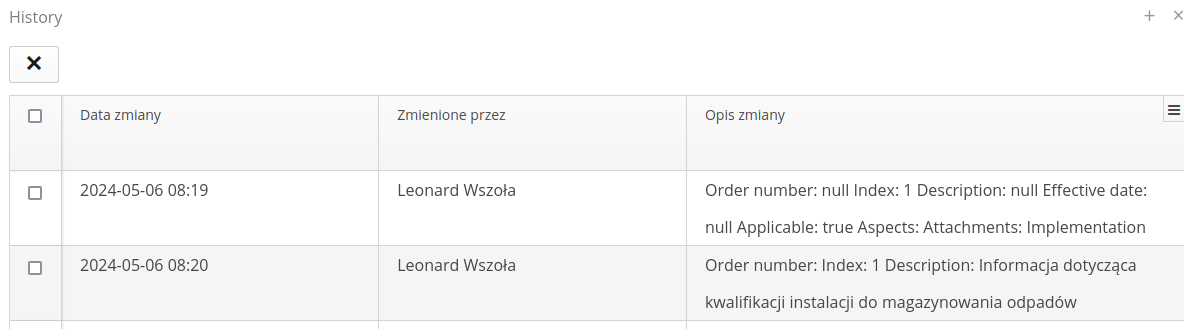
The Files/Aspects lists allow you to add this information to a given article. We can use additional buttons in these lists:
-
Add/Remove - add/remove an object from the list
-
Download file - download a given file
-
PDF file preview - preview any PDF file inside the application
Integration with the SEJM of the Republic of Poland
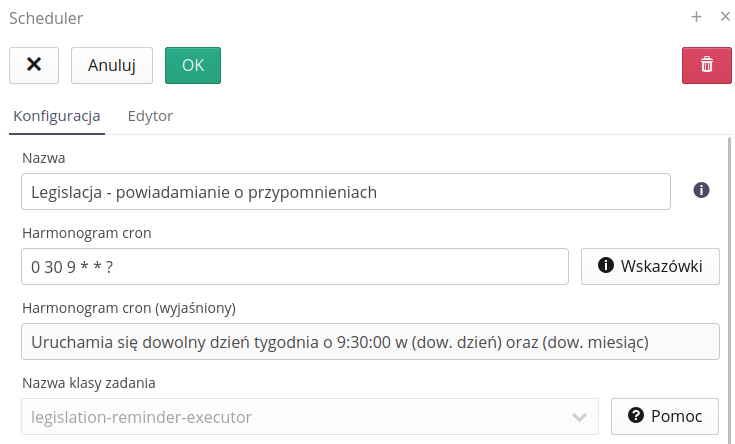
An additional functionality available to users from Poland is IT integration with the system for publishing legal acts of the Sejm of the Republic of Poland. Using the prepared scheduler, we can automatically search legal acts published on government websites and notify users about the appearance of new legal acts that meet the search criteria.
An example scheduler setting is shown below. It searches for the keywords "OHS" anywhere in the published document - i.e. in the name, description and categories to which it was assigned by the IT systems of the Sejm of the Republic of Poland.
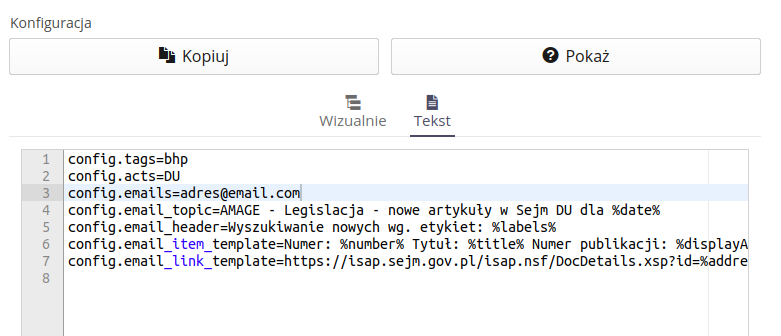
An example notification result, which can be freely configured, contains information about the name of the article along with a direct link to the document on the publication’s website

ISO
The ISO section allows you to operate and record records that comply with certain ISO procedures.
Registers available in the system
-
Corrective actions - register of corrective actions
-
Risks and opportunities - register of risks/opportunities with criticality analysis
-
Rationation applications - a register of rationalization applications
All of these registers have their own data definitions, execution traceability and sub-tasks within each register.
| In the case of creating new register entries, it is required to define automatic counters that will assign numbers to individual documents. |
If you do not define the counters, you will get a jn message when you try to create any register.

No default counter defined. … says about the need to define counters. To do this, go to the configuration section and in the general settings select the Counters tab. There, in the ISO section, we indicate which counters (or created new ones) will be responsible for the automatic numbering of documents.
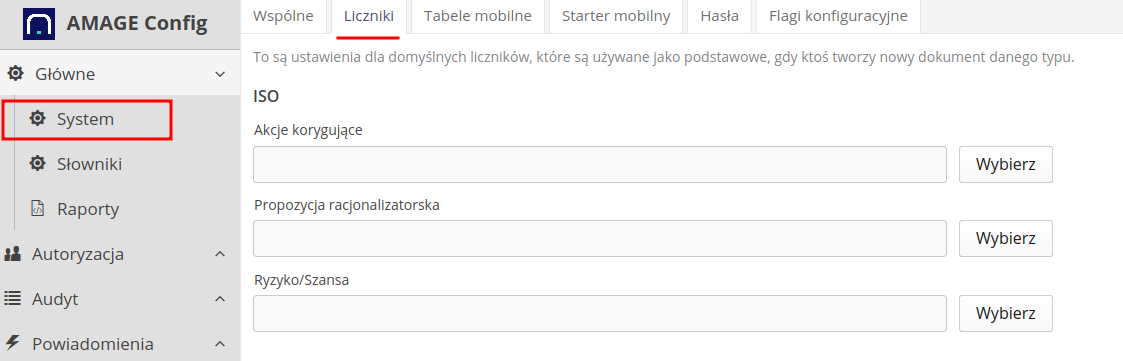
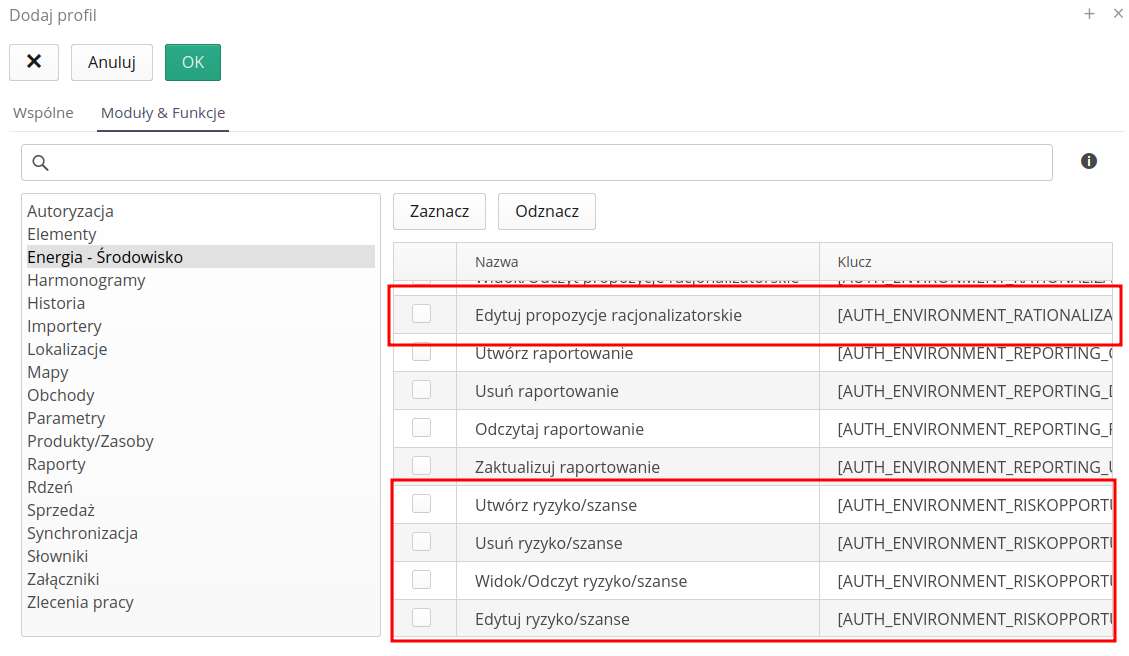
In the case of this module, we also have the option of specifying permissions to access individual sections/actions. Authorizations are available in the "Energy - Environment" module and allow you to specify authorizations for individual operations: view/create/edit/delete.
The ISO module also has its own dictionary elements. They are available collectively in the system configuration view, but also directly in the context menu of registry views.
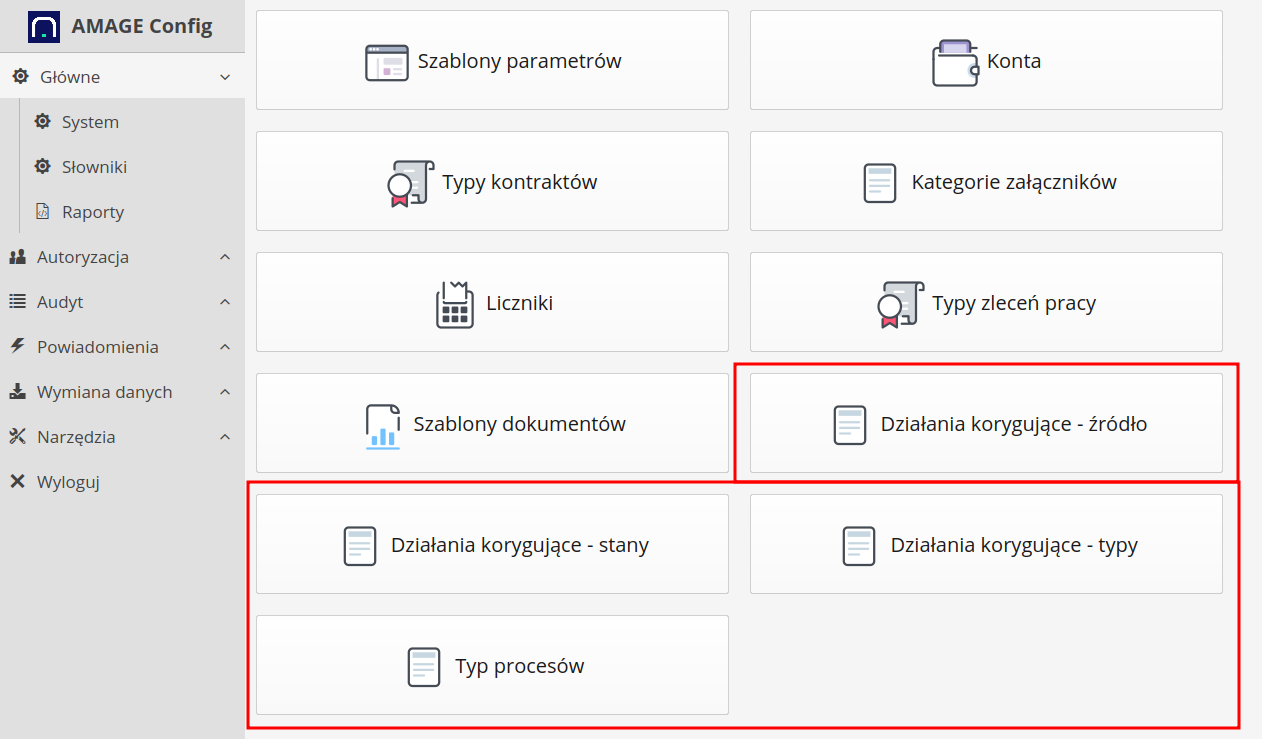
Additional dictionaries:
-
Corrective actions - source - allows you to specify a dictionary of corrective action sources
-
Corrective actions - states - definition of corrective action states
-
Corrective actions - types - type of corrective action
-
Type of ISO processes - types of ISO processes to be defined within each of the registers.
ISO - register of Corrective Actions
The register of corrective actions allows you to enter and monitor this type of register.
The basic view shows a list of all events. Using dedicated buttons, we can select registers created by the current user or assigned to him.
Additional filters are located in the side dock and allow for additional filter definitions.
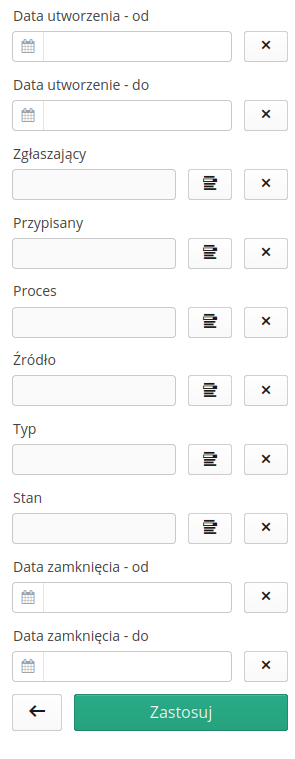
Creation of a new Corrective Action Register
The form for creating a new record contains all the basic information about this type of data. It is divided into individual tabs
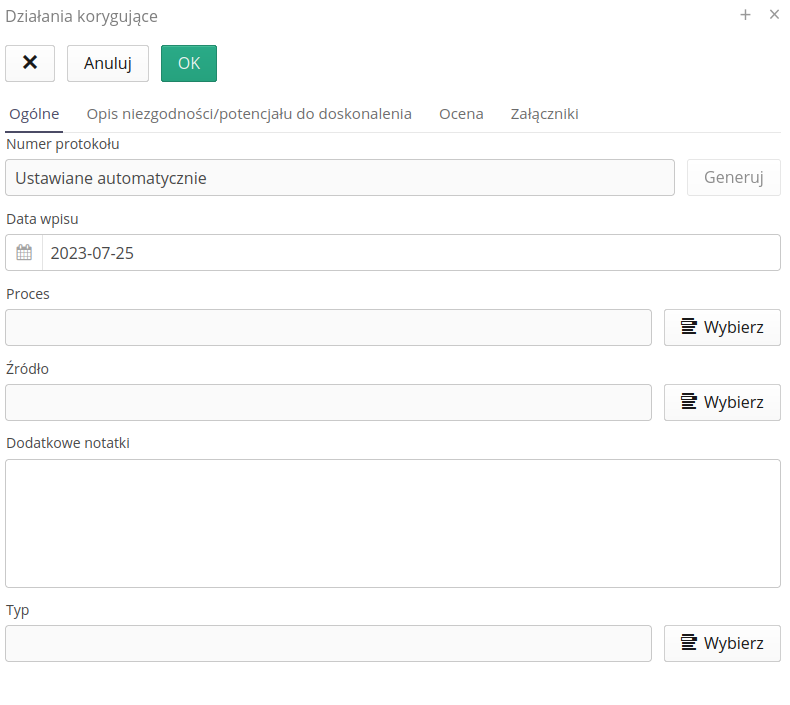
-
Protocol number - automatically assigned protocol number
-
Date of entry - date of entry into the register
-
Process - ISO process selected from the dictionary
-
Source - source - dictionary data
-
Additional notes - additional notes describing the operation
-
Type - action type - dictionary
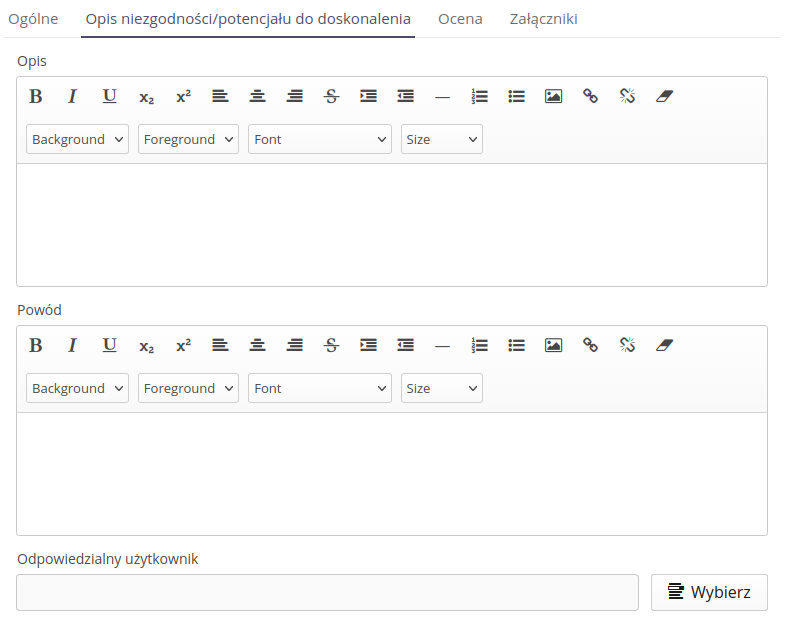
-
Description - detailed description of the operation
-
Reason - the reason for the action
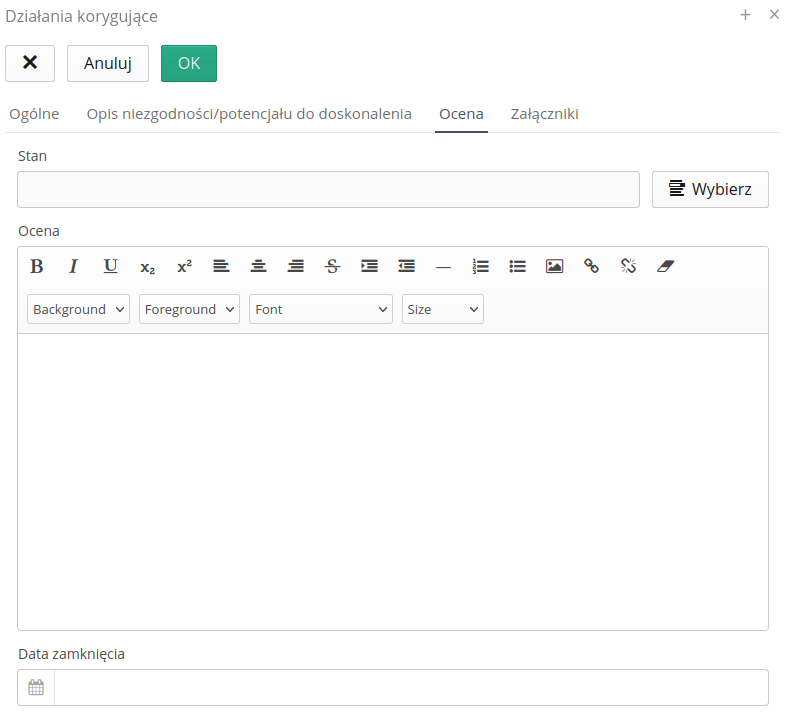
-
Status - current state of operation - selection from the dictionary
-
Assessment - performance evaluation
-
Closing date - date of final closing of the activity
Additionally, attachments regarding this action.
Registry details
After filling in the data, we can view them in aggregate and detailed form. After selecting a given record, we go to the detailed view. The information entered in the authoring form is contained in the individual tabs.
In addition, we have a list of detailed tasks that can be created within a given registry. They allow you to track and divide work between individuals.
The log history shows information about log data changes over time and creating/editing detailed tasks. Using this tab, we can also edit parameters.
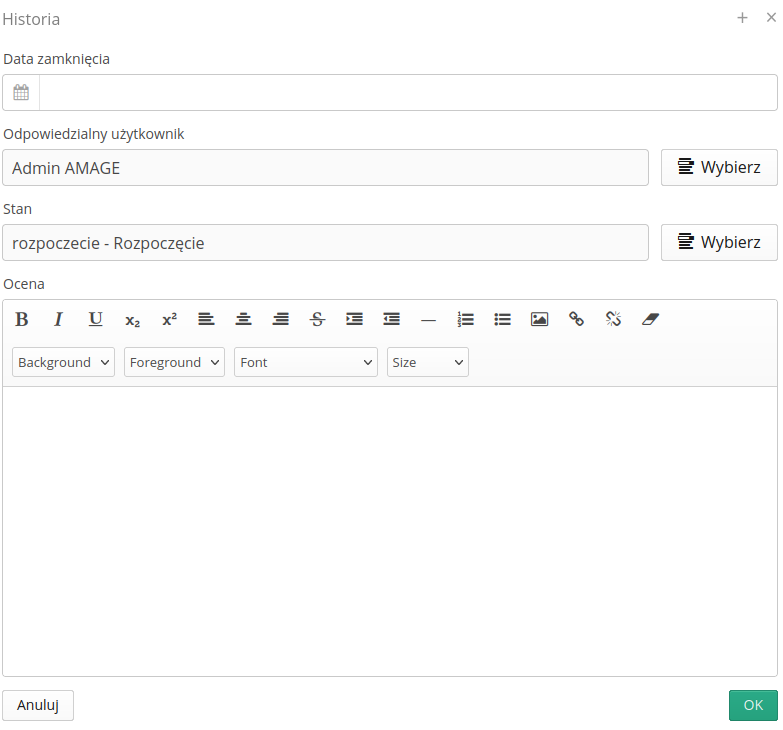
By adding a historical record, we can execute/register individual data.
-
Close date - register closing date
-
Responsible - change of responsible person
-
State - change of the register state
-
Evaluation - final assessment of the process implementation
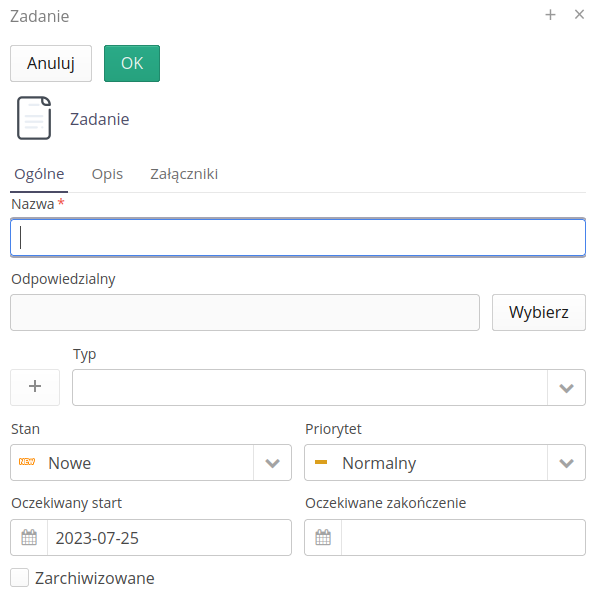
The new task form is simplified compared to the main view of work orders. Allows you to enter basic job data.
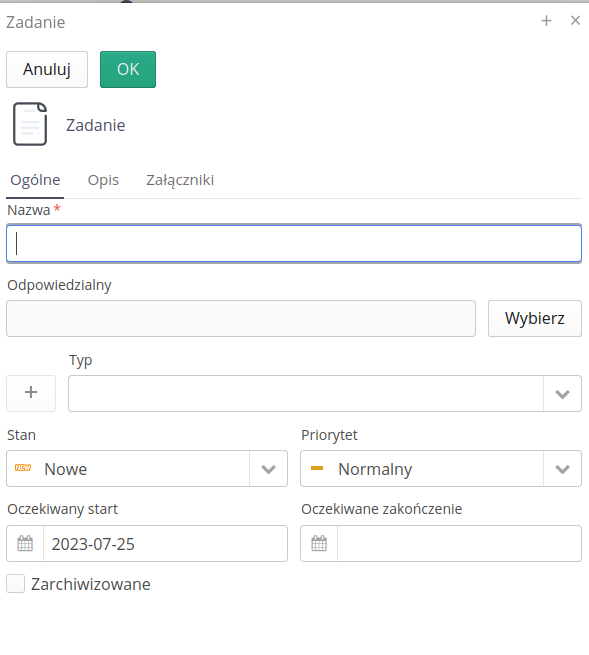
-
Name/description - task name/description
-
Responsible - responsible person
-
Type, Status, Priority - job type/status and priority
-
Expected start/end - start/end times
The task details view is displayed in a simplified way and we have the ability to quickly change the status of the task and basic editing/saving additional attachments to the task.
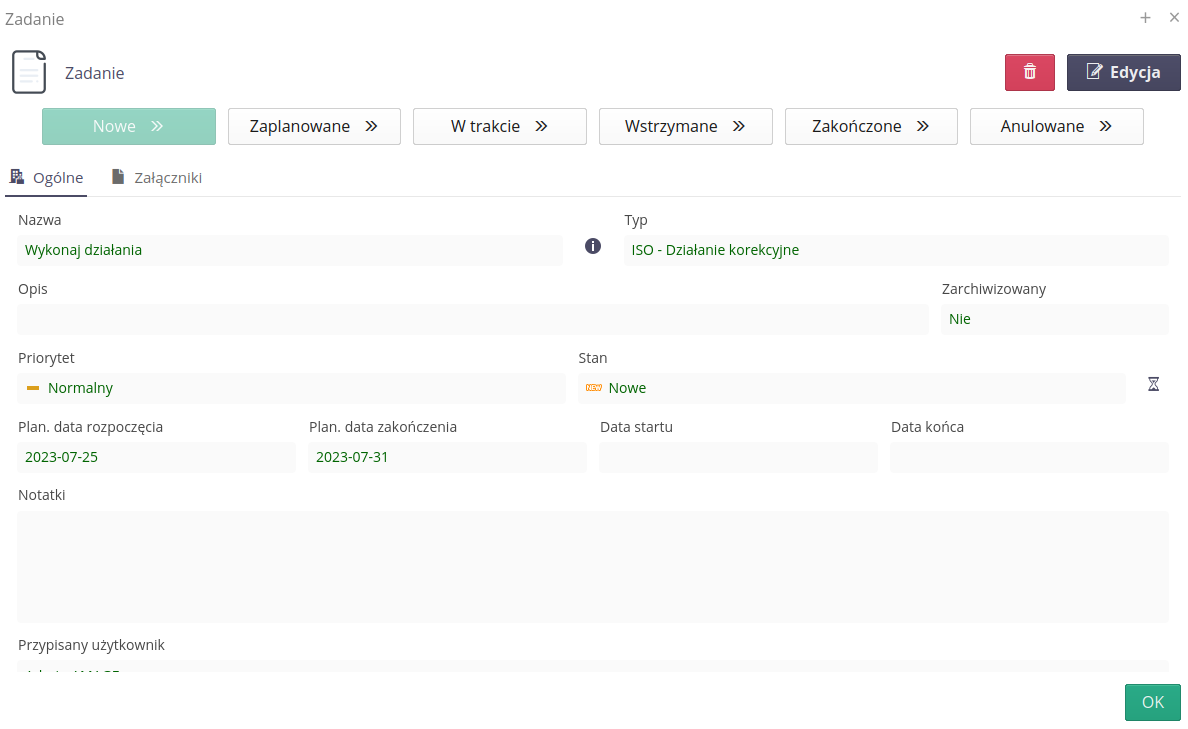
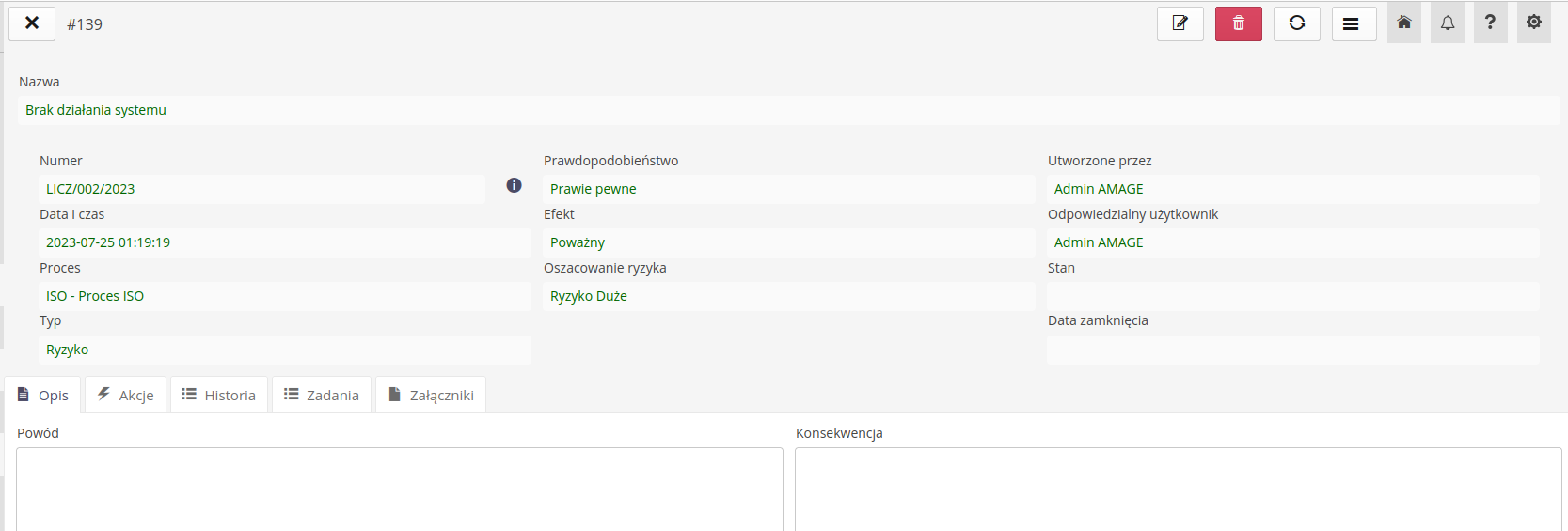
ISO - Register of risks and opportunities
The register of risks/opportunities allows you to enter and monitor this type of register.
The basic view shows a list of all events. Using dedicated buttons, we can select registers of a specific type: Risk/Opportunity.
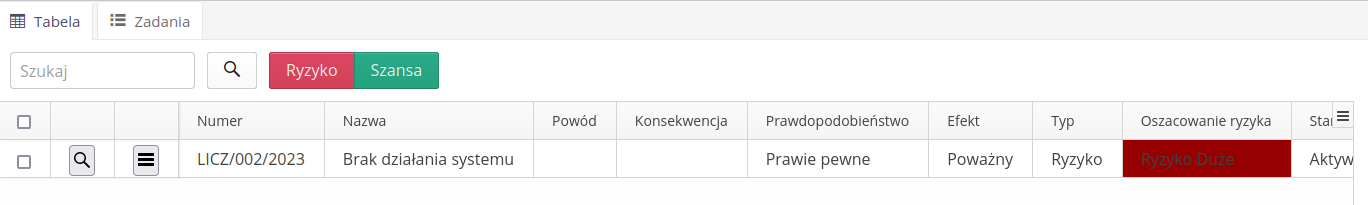
Additional filters are located in the side dock and allow for additional filter definitions.
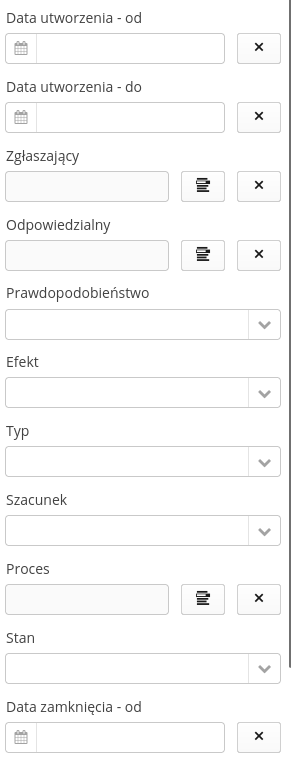
Creation of a new risk/opportunity register
Creating a new register allows you to define and enter all key data
-
Name - name of the risk/opportunity
-
Protocol number - automatically assigned
-
Reason - description of the reason for the entry
-
Consequence - description of the consequences
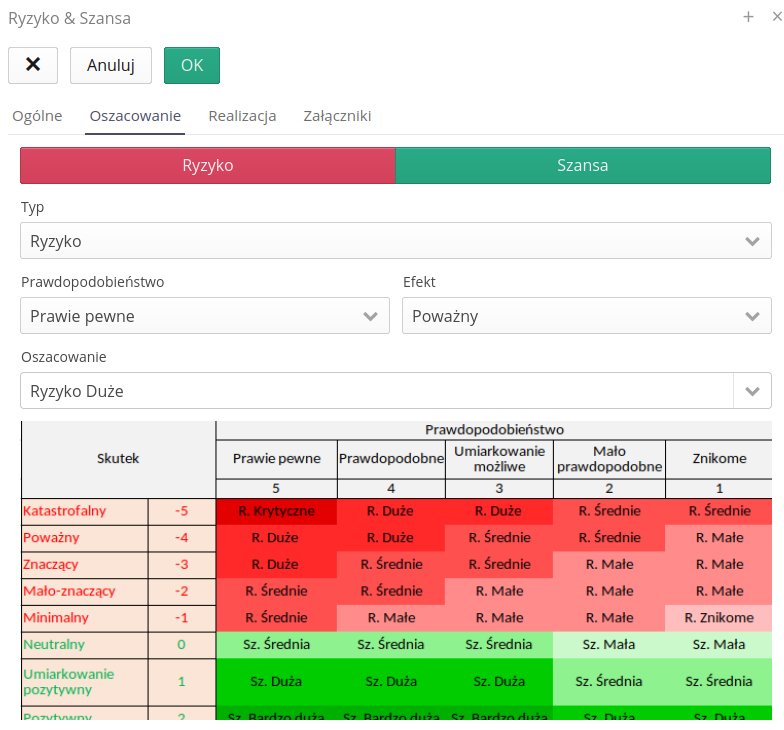
-
Risk/Opportunity - selection of register type
-
Probability - determination of probability
-
Effect - determination of the effect of not implementing actions
-
Estimation - automatic criticality estimation
-
Risk table - auxiliary risk table
-
Responsible - the person responsible for the implementation
-
Process - selection of the process in which the risk/opportunity arose
-
Status - status of implementation
-
Closing date - closing date
-
Implemented activities - summary of implemented activities
Additional attachments and information can also be added to the register.
Viewing registry details
After filling in the data, we can view them in aggregate and detailed form. After selecting a given record, we go to the detailed view. The information entered in the authoring form is contained in the individual tabs.
In addition, we have a list of detailed tasks that can be created within a given registry. They allow you to track and divide work between individuals.
Historical record can be entered directly from the history view.
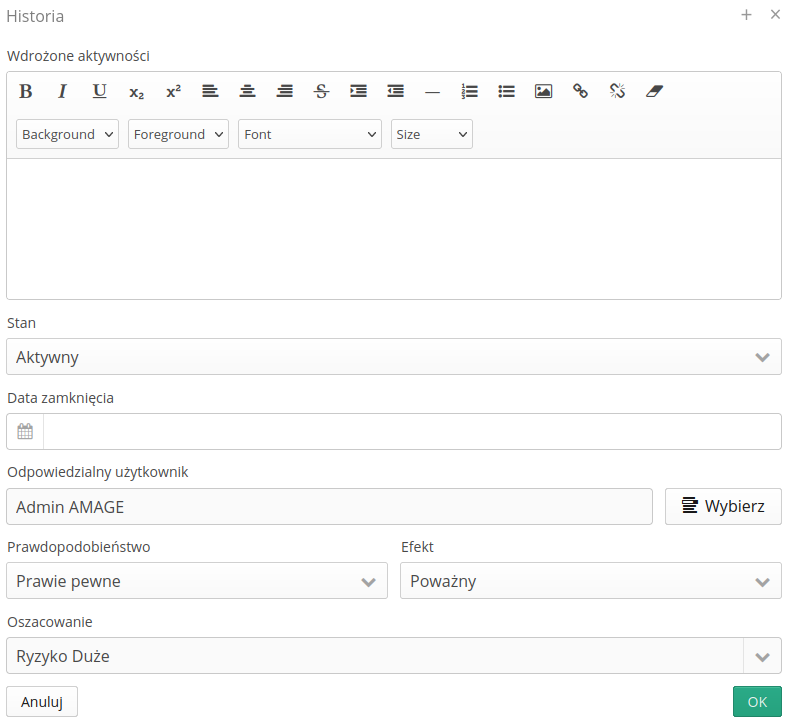
-
Implemented activities - activity definition
-
State - state change
-
Closing date - specifying the closing date
-
Responsible - change of assigned person
-
Probability - parameter change
-
Effect - parameter change
-
Estimation - parameter change
The new task form is simplified compared to the main view of work orders. Allows you to enter basic job data.
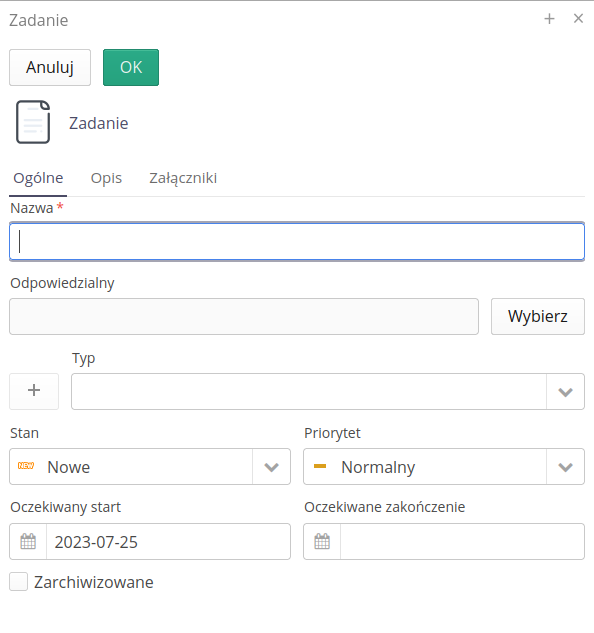
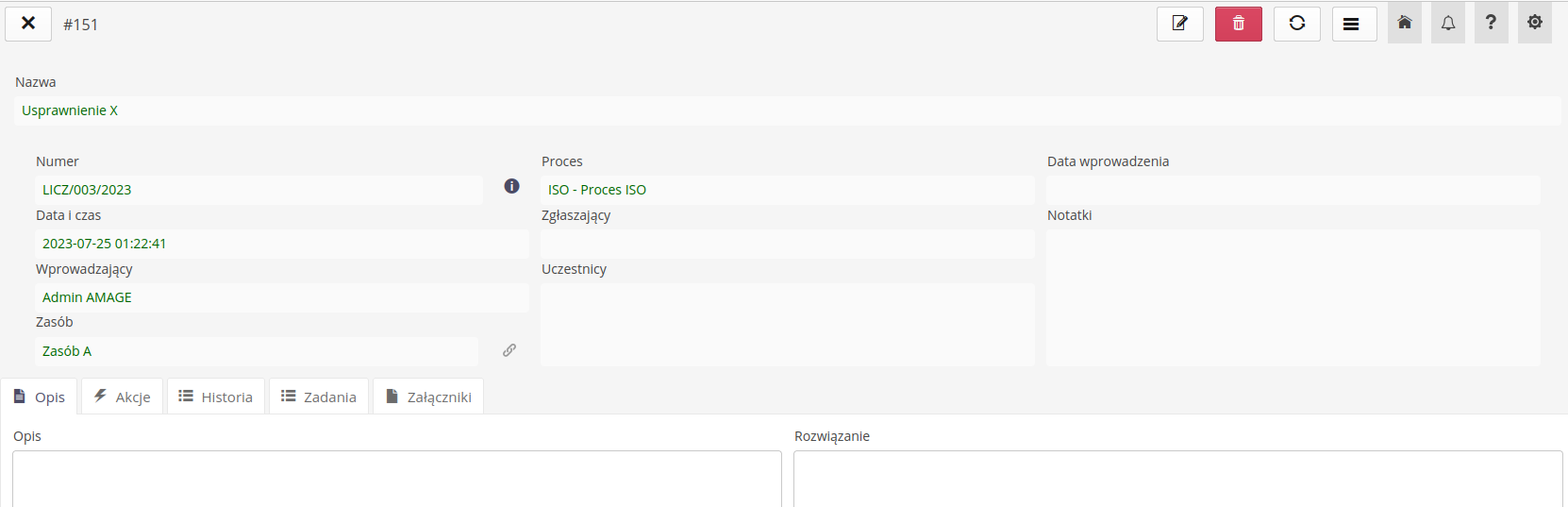
ISO - Register of rationalization proposals
The register of rationalization applications allows for the introduction and monitoring of this type of register. The basic view shows a list of all events.
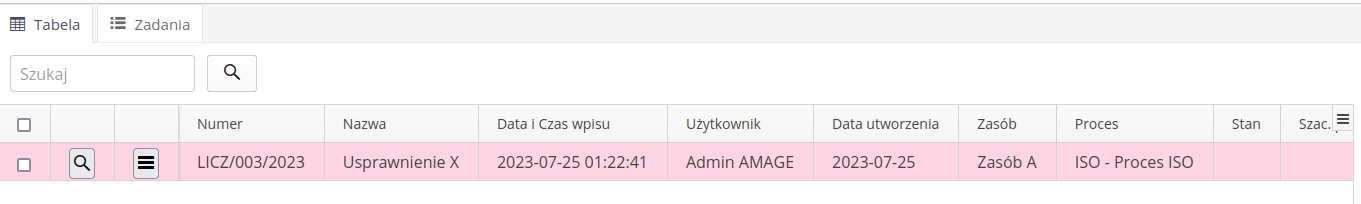
Additional filters are located in the side dock and allow for additional filter definitions.
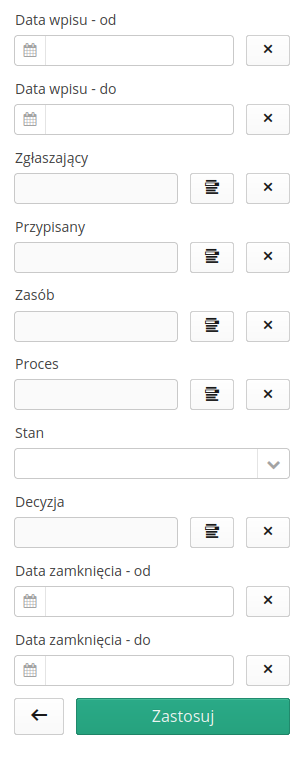
Additional dictionaries necessary to enter records can also be accessed from the context menu of a given register view. Here you can access the register of decision types and ISO process types.
Creation of a new register of applications
Creating a new register allows you to define and enter all key data
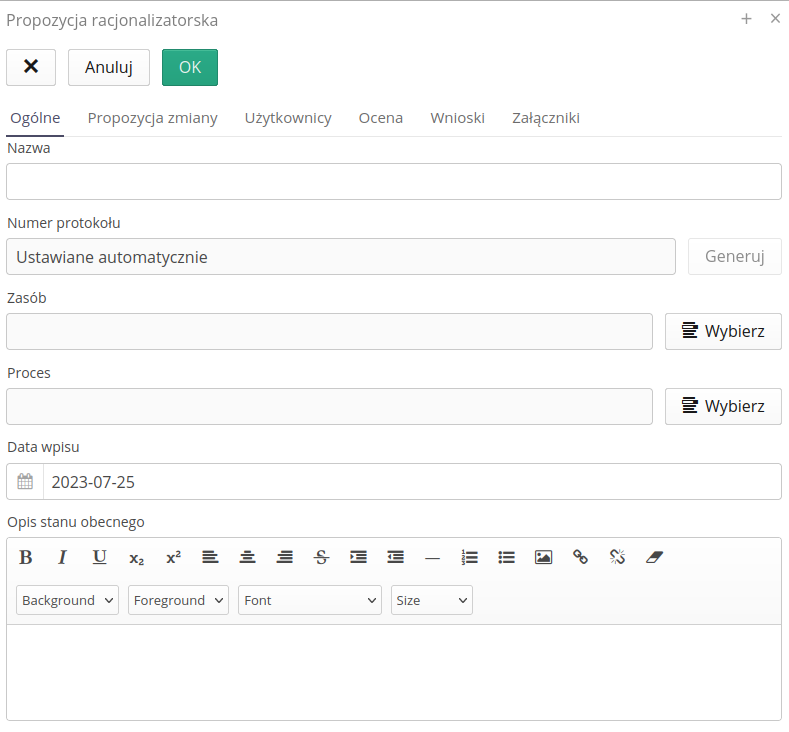
-
Name - name of the application
-
Protocol number - automatically assigned
-
Resource - indicated resource to which the application relates
-
Process - indicated process to which the application relates
-
Entry date - date of entry
-
Description of the current state - extended description of the current state
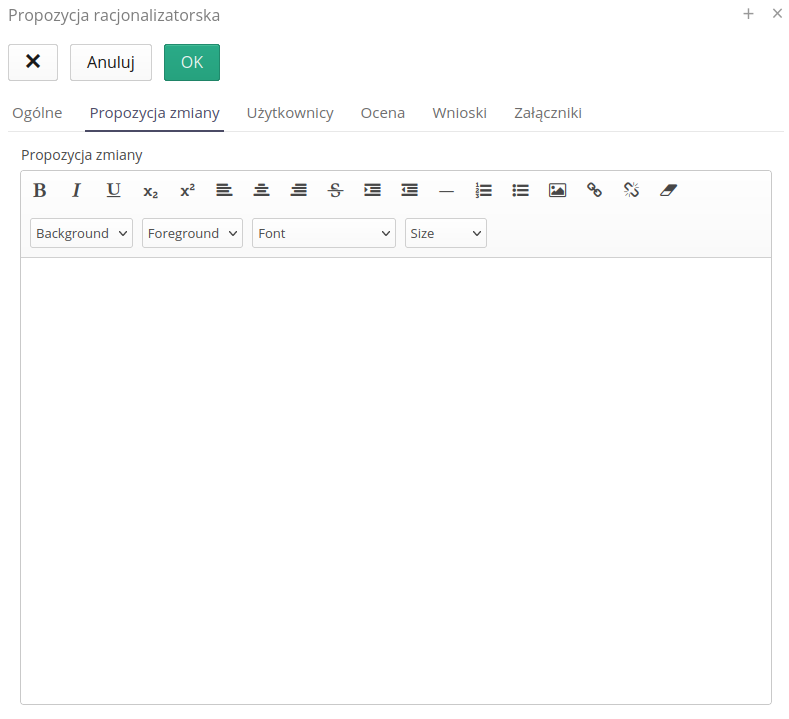
-
Change proposal - extended change proposal
-
Reporting User - key reporting/applicant person
-
Participating users - participants in the process (co-applicants/authors)
-
Decision - the decision regarding the record.
-
Responsible - appointing a responsible person
-
Status - current state of the register
-
Estimated start/end - estimated completion dates
-
Notes - additional notes
-
Close date - register closing date
-
Conclusions - descriptive conclusions from the implementation/rejection of the application
Viewing registry details
After filling in the data, we can view them in aggregate and detailed form. After selecting a given record, we go to the detailed view. The information entered in the authoring form is contained in the individual tabs.
In addition, we have a list of detailed tasks that can be created within a given registry. They allow you to track and divide work between individuals.
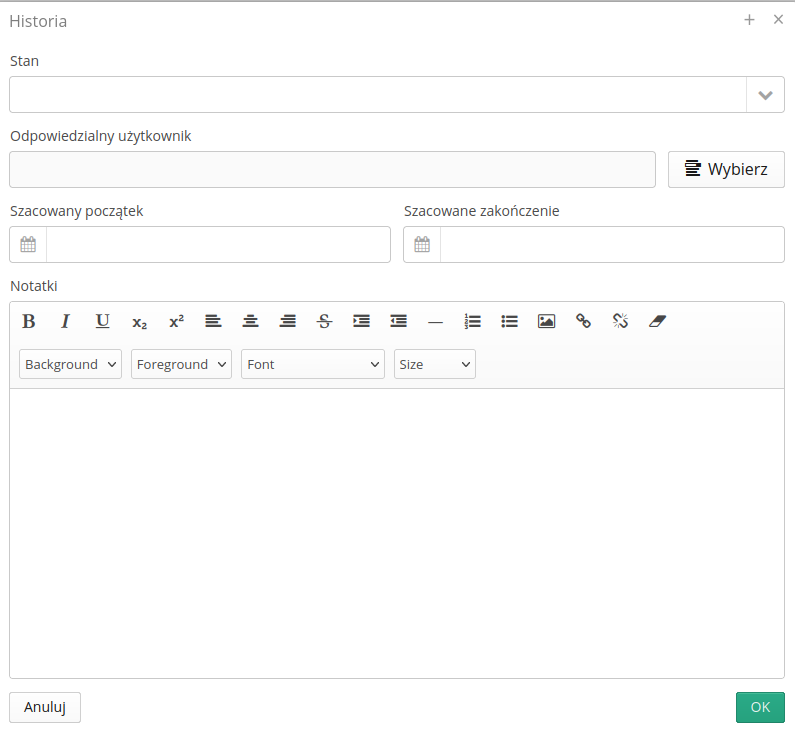
The available actions within the historical entry allow you to define the record and change basic data such as:
-
Status - current status of the application
-
Responsible user - change of user
-
Estimated start/end - estimated start/end of execution
-
Notes - additional notes
The new task form is simplified compared to the main view of work orders. Allows you to enter basic job data.